D4A523
Gene name |
Nlrp3 |
Protein name |
NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 |
Names |
Cold autoinflammatory syndrome 1 protein homolog, Cryopyrin, Mast cell maturation-associated-inducible protein 1, PYRIN-containing APAF1-like protein 1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:287362 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
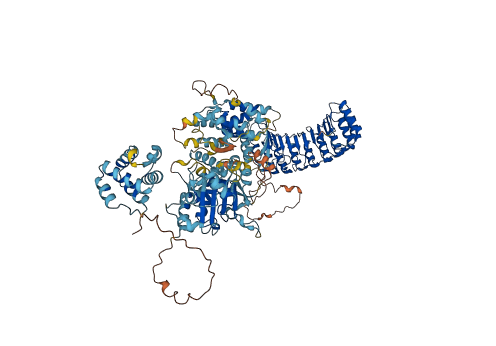
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-93 (PYRIN domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for D4A523
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-D4A523-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for D4A523
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs106539953 | 213 | H>R | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with D4A523
10 regional properties for D4A523
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 738 - 761 | IPR001611-1 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 796 - 818 | IPR001611-2 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 852 - 875 | IPR001611-3 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 909 - 932 | IPR001611-4 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 966 - 990 | IPR001611-5 |
| domain | DAPIN domain | 1 - 93 | IPR004020 |
| domain | NACHT nucleoside triphosphatase | 218 - 417 | IPR007111 |
| domain | NACHT-associated domain | 137 - 208 | IPR029495 |
| domain | NOD2, winged helix domain | 463 - 518 | IPR041075 |
| domain | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein, helical domain HD2 | 520 - 644 | IPR041267 |
Functions
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| inflammasome complex | A cytosolic protein complex that is capable of activating caspase-1. |
| NLRP3 inflammasome complex | An inflammasome complex that consists of three components, NLRP3 (NALP3), PYCARD and caspase-1. It is activated upon exposure to whole pathogens, as well as a number of structurally diverse pathogen- and danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs and DAMPs) and environmental irritants. Whole pathogens demonstrated to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome complex include the fungi Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacteria that produce pore-forming toxins, including Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, and viruses such as Sendai virus, adenovirus, and influenza virus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
30 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase in the context of an apoptotic process. |
| acute inflammatory response | Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to peptidoglycan | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptidoglycan stimulus. Peptidoglycan is a bacterial cell wall macromolecule. |
| defense response to Gram-positive bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-positive bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response | The movement of a leukocyte within or between different tissues and organs of the body contributing to an inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of acute inflammatory response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an acute inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-1 beta production. |
| negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form the NLRP3 inflammasome complex, occurring at the level of an individual cell. |
| positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the activity of a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in the apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of cytokine production that contributes to an immune response. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-1 beta production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-13 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-13 production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-4 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-4 production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-5 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-5 production. |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T-helper 17 cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production. |
| positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T-helper 2 cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of type 2 immune response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a type 2 immune response. |
| regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response, the immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A6QLE5 | NLRP3 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q96P20 | NLRP3 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| E9Q5R7 | Nlrp12 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8R4B8 | Nlrp3 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| B0FPE9 | NLRP3 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKMMSVRCKL | AQYLEDLEDV | DLKKFKMHLE | DYPPEKGCVP | IPRGQMEKAD | HLDLATLMID |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FNGEEKAWGM | AVWIFAAINR | RDLWEKAKKD | QPEWNDACTS | NLSMVCQEDS | LEEEWIGLLG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| YLSRISICKK | KKDYCKIYRR | HVRSRFYSIK | DRNARLGESV | DLNRRYTQLQ | LVKEHPSKQE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| REHELLTIGR | TKMWDRPMSS | LKLELLFEPE | DEHLEPVHTV | VFQGAAGIGK | TILARKIMLD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| WALGKLFKDK | FDYLFFIHCR | EVSLRAPKSL | ADLIISCWPD | PNPPVCKILC | KPSRILFLMD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GFDELQGAFD | EHIEEVCTDW | QKAVRGDILL | SSLIRKKLLP | KASLLITTRP | VALEKLQHLL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DHPRHVEILG | FSEAKRKEYF | FKYFSNELQA | REAFRLIQEN | EILFTMCFIP | LVCWIVCTGL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| KQQMETGKSL | AQTSKTTTAV | YVFFLSSLLQ | SRGGIEEHLF | SAYLPGLCSL | AADGIWNQKI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LFEECDLRKH | GLQKTDVSAF | LRMNVFQKEV | DCERFYSFSH | MTFQEFFAAM | YYLLEEEEEG |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VTVRKGPEGC | SDLLNRDVKV | LLENYGKFEK | GYLIFVVRFL | FGLVNQERTS | YLEKKLSCKI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| SQQVRLELLK | WIEVKAKAKK | LQRQPSQLEL | FYCLYEMQEE | DFVQSAMGHF | PKIEINLSTR |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| MDHVVSSFCI | KNCHRVKTLS | LGFLHNSPKE | EEEEKRGSQP | LDQVQCVFPD | PHVACSSRLV |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| NCCLTSSFCR | GLFSSLSTNQ | SLTELDLSDN | TLGDPGMRVL | CEALQHPGCN | IQRLWLGRCG |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| LTHQCCFNIS | SVLSSSQKLV | ELDLSDNALG | DFGVRLLCVG | LKHLLCNLQK | LWLVSCCLTS |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| ACCQDLALVL | SSNHSLTRLY | IGENALGDSG | VQVLCEKMKD | PQCNLQKLGL | VNSGLTSLCC |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| SALTSVLKTN | QNLTHLYLRS | NALGDMGLKL | LCEGLLHPDC | KLQMLELDNC | SLTSHSCWDL |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| STILTHNQSL | RKLNLSNNDL | GDLCVVTLCE | VLKQQGCLLQ | SLQLGEMYLN | CETKRTLEAL |
| 1030 | |||||
| QEEKPELTVV | FEISW |