D4A280
Gene name |
Pak5 (Pak7) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 |
Names |
p21-activated kinase 5, PAK-5, p21-activated kinase 7, PAK-7 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:311450 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
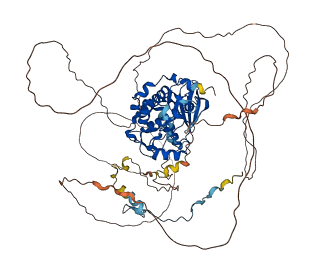
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
448-699 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
584-607 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
425-716 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p21-activated kinase 5) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Ching YP et al. (2003) "Identification of an autoinhibitory domain of p21-activated protein kinase 5", The Journal of biological chemistry, 278, 33621-4
- Bautista L et al. (2020) "p21-Activated Kinases in Thyroid Cancer", Endocrinology, 161,
- Ha BH et al. (2012) "Type II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are regulated by an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 16107-12
- Chong C et al. (2001) "The mechanism of PAK activation. Autophosphorylation events in both regulatory and kinase domains control activity", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 17347-53
- Wang J et al. (2011) "Structural insights into the autoactivation mechanism of p21-activated protein kinase", Structure (London, England : 1993), 19, 1752-61
- Lei M et al. (2000) "Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch", Cell, 102, 387-97
- Totaro A et al. (2007) "Identification of an intramolecular interaction important for the regulation of GIT1 functions", Molecular biology of the cell, 18, 5124-38
- Rousseau V et al. (2003) "A new constitutively active brain PAK3 isoform displays modified specificities toward Rac and Cdc42 GTPases", The Journal of biological chemistry, 278, 3912-20
- Dan C et al. (2002) "PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells", Molecular and cellular biology, 22, 567-77
- Kaur R et al. (2005) "Activation of p21-activated kinase 6 by MAP kinase kinase 6 and p38 MAP kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 3323-30
- Gao J et al. (2013) "Substrate and inhibitor specificity of the type II p21-activated kinase, PAK6", PloS one, 8, e77818
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for D4A280
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-D4A280-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for D4A280
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for D4A280 | |||||
No associated diseases with D4A280
5 regional properties for D4A280
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CRIB domain | 10 - 62 | IPR000095 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 448 - 699 | IPR000719 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 454 - 478 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK5, catalytic domain | 425 - 716 | IPR028754 |
| domain | p21 activated kinase binding domain | 9 - 55 | IPR033923 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
9 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| learning | Any process in an organism in which a relatively long-lasting adaptive behavioral change occurs as the result of experience. |
| locomotory behavior | The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions. |
| memory | The activities involved in the mental information processing system that receives (registers), modifies, stores, and retrieves informational stimuli. The main stages involved in the formation and retrieval of memory are encoding (processing of received information by acquisition), storage (building a permanent record of received information as a result of consolidation) and retrieval (calling back the stored information and use it in a suitable way to execute a given task). |
| negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAP kinase (MAPK) cascade. |
23 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q12469 | SKM1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SKM1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q08E52 | PAK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q7YQL4 | PAK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| Q9VXE5 | mbt | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK mbt | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q13153 | PAK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13177 | PAK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O75914 | PAK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O96013 | PAK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NQU5 | PAK6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9P286 | PAK5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8CIN4 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O88643 | Pak1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61036 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3ULB5 | Pak6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C015 | Pak5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BTW9 | Pak4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q64303 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35465 | Pak1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62829 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O54748 | Stk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17850 | pak-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase pak-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5EGQ3 | max-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase max-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EFU0 | pak-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase pak-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MFGKKKKKIE | ISGPSNFEHR | VHTGFDPQEQ | KFTGLPQQWH | SLLADTANRP | KPMVDPSCIT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PIQLAPMKTI | VRGNKSCKES | SINGLLEDFD | NISVTRSNSL | RKESPPTPDQ | GAASRIQGHS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EENGFITFSQ | YSSESDTTTD | YTTEKYRDRS | LYGDDLDLYY | RGSHAAKQNG | HAMKMKHGDA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| YYPEMKPLKS | DLARFPVDYH | THLDSLSKAS | EYGDLKWDYQ | RASSSSPLDY | SFQLTPSRTA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GTSRCSKESL | AYSESDWGPS | FDDYDRRPKS | SYLHQTSPQP | AMRQRSKSGS | GLQEPMMPFG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ASAFKTHPQG | HSYNSYTYPR | LSEPTMCIPK | VDYDRAQMVF | SPPLSGSDTY | PRGPTKLPQS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| QSKVGYSSSS | HQYPGYHKAS | LYHHPSLQTS | SQYISTASYL | SSLSISSSTY | PPPSWGSSSD |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QQPSRVSHEQ | FRAALQLVVS | PGDPREYLDN | FIKIGEGSTG | IVCIATEKHT | GKQVAVKKMD |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LRKQQRRELL | FNEVVIMRDY | HHDNVVDMYN | SYLVGDELWV | VMEFLEGGAL | TDIVTHTRMN |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| EEQIATVCLS | VLKALSYLHN | QGVIHRDIKS | DSILLTSDGR | IKLSDFGFCA | QVSKEVPKRK |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| SLVGTPYWMA | PEVISRLPYG | TEVDIWSLGI | MVIEMIDGEP | PYFNEPPLQA | MRRIRDSLPP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | |
| RVKDLHKVSS | MLRGFLDLML | VREPSQRATA | QELLGHPFLK | LAGPPSCIVP | LMRQYRHH |