D3ZPX4
Gene name |
Plxna3 |
Protein name |
Plexin-A3 |
Names |
|
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:309280 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1294-1842 (Plexin, RasGAP domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
1294-1842 (Plexin, RasGAP domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
1294-1842 (Plexin, RasGAP domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- He H et al. (2009) "Crystal structure of the plexin A3 intracellular region reveals an autoinhibited conformation through active site sequestration", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 15610-5
- Takahashi T et al. (2001) "Plexina1 autoinhibition by the plexin sema domain", Neuron, 29, 429-39
- Wang Y et al. (2012) "Plexins are GTPase-activating proteins for Rap and are activated by induced dimerization", Science signaling, 5, ra6
- Yokoyama N et al. (2005) "The C terminus of RON tyrosine kinase plays an autoinhibitory role", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 8893-900
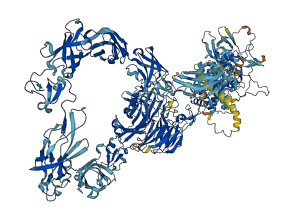
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for D3ZPX4
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-D3ZPX4-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for D3ZPX4
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for D3ZPX4 | |||||
No associated diseases with D3ZPX4
12 regional properties for D3ZPX4
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Sema domain | 6 - 489 | IPR001627 |
| repeat | Plexin repeat | 491 - 531 | IPR002165-1 |
| repeat | Plexin repeat | 638 - 678 | IPR002165-2 |
| domain | IPT domain | 840 - 934 | IPR002909-1 |
| domain | IPT domain | 935 - 1021 | IPR002909-2 |
| domain | IPT domain | 1023 - 1123 | IPR002909-3 |
| domain | IPT domain | 1125 - 1220 | IPR002909-4 |
| domain | PSI domain | 491 - 541 | IPR016201-1 |
| domain | PSI domain | 638 - 685 | IPR016201-2 |
| domain | PSI domain | 786 - 839 | IPR016201-3 |
| domain | Plexin, TIG domain 2 | 692 - 785 | IPR041362 |
| domain | Plexin, cytoplasmic RhoGTPase-binding domain | 1464 - 1576 | IPR046800 |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| semaphorin receptor complex | A stable binary complex of a neurophilin and a plexin, together forming a functional semaphorin receptor. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| semaphorin receptor activity | Combining with a semaphorin, and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| branchiomotor neuron axon guidance | The process in which a branchiomotor neuron growth cone is directed to a specific target site. Branchiomotor neurons are located in the hindbrain and innervate branchial arch-derived muscles that control jaw movements, facial expression, the larynx, and the pharynx. |
| facial nerve structural organization | The process that contributes to the act of creating the structural organization of the facial nerve. This process pertains to the physical shaping of a rudimentary structure. This sensory and motor nerve supplies the muscles of facial expression and the expression and taste at the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The principal branches are the superficial opthalmic, buccal, palatine and hyomandibular. The main trunk synapses within pterygopalatine ganglion in the parotid gland and this ganglion then gives of nerve branches which supply the lacrimal gland and the mucous secreting glands of the nasal and oral cavities. |
| hippocampus development | The progression of the hippocampus over time from its initial formation until its mature state. |
| negative chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell or organism towards a lower concentration of a chemical. |
| negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of axon extension involved in axon guidance. |
| negative regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell adhesion. |
| neuron projection extension | Long distance growth of a single neuron projection involved in cellular development. A neuron projection is a prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| neuron projection guidance | The process in which the migration of a neuron projection is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| positive regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis. |
| positive regulation of cytoskeleton organization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
| pyramidal neuron development | The progression of a pyramidal neuron from its initial formation to its mature state. |
| regulation of cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that modulates the rate of GTP hydrolysis by a GTPase. |
| semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance | Any semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway that is involved in axon guidance. |
| trigeminal nerve structural organization | The process that contributes to the act of creating the structural organization of the oculomotor nerve. This process pertains to the physical shaping of a rudimentary structure. The trigeminal nerve is composed of three large branches. They are the ophthalmic (V1, sensory), maxillary (V2, sensory) and mandibular (V3, motor and sensory) branches. The sensory ophthalmic branch travels through the superior orbital fissure and passes through the orbit to reach the skin of the forehead and top of the head. The maxillary nerve contains sensory branches that reach the pterygopalatine fossa via the inferior orbital fissure (face, cheek and upper teeth) and pterygopalatine canal (soft and hard palate, nasal cavity and pharynx). The motor part of the mandibular branch is distributed to the muscles of mastication, the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric. The mandibular nerve also innervates the tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani muscles. The sensory part of the mandibular nerve is composed of branches that carry general sensory information from the mucous membranes of the mouth and cheek, anterior two-thirds of the tongue, lower teeth, skin of the lower jaw, side of the head and scalp and meninges of the anterior and middle cranial fossae. |
27 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q769I5 | MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| A0M8S8 | MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | PR |
| Q04912 | MST1R | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08581 | MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O43157 | PLXNB1 | Plexin-B1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| Q9HCM2 | PLXNA4 | Plexin-A4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O75051 | PLXNA2 | Plexin-A2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9UIW2 | PLXNA1 | Plexin-A1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| O15031 | PLXNB2 | Plexin-B2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9ULL4 | PLXNB3 | Plexin-B3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51805 | PLXNA3 | Plexin-A3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9QY40 | Plxnb3 | Plexin-B3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UH93 | Plxnd1 | Plexin-D1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70207 | Plxna2 | Plexin-A2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| B2RXS4 | Plxnb2 | Plexin-B2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CJH3 | Plxnb1 | Plexin-B1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9QZC2 | Plxnc1 | Plexin-C1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q80UG2 | Plxna4 | Plexin-A4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70206 | Plxna1 | Plexin-A1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV SS |
| P70208 | Plxna3 | Plexin-A3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV SS |
| Q2QLE0 | MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P97523 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| D3ZLH5 | Plxnb3 | Plexin-B3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6BEA0 | plxna4 | Plexin-A4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| B0S5N4 | plxna3 | Plexin A3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MHTVCLLPLL | FFTIGGCLGS | SRPFRTFVVT | DTTLTHLAVH | RVTGEVFVGA | VNRVFKLASN |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LTELRAHVTG | PIEDNARCYP | PPSMRVCSHR | LVPVDNVNKL | LLIDYAARRL | VACGSIWQGI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CQFLRLDDLF | KLGEPHHRKE | HYLSGAQEPD | SMAGVIVEQG | QGPSKLFVGT | AVDGKSEYFP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TLSSRKLIDD | EDSGDMFSLV | YQDEFVSSQI | KIPSDTLSLY | PAFDIYYIYG | FVSASFVYFL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TLQLDTQQTL | LDTAGEKFFT | SKIVRMCAGD | SEFYSYVEFP | IGCSWRGVEY | RLVQSAHLAK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PGLLLAQALG | VPADEDVLFT | IFSQGQKNRA | NPPRQTILCL | FTLSSINAHI | RRRIQSCYRG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EGTLALPWLL | NKELPCINTP | MQINGNFCGL | VLNQPLGGLH | VIEGLPLLAD | STDGMASVAA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YTYHQHSVVF | IGTRSGNLKK | VRVDGSQDAQ | LYETVSVVQG | TPILRDLLFS | PDHRHIYLLS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EKQVSQLPVE | TCEQYLSCAA | CLGSGDPHCG | WCVLQHRCCR | EGACPGASAP | HGFAEELNKC |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| IQVRVRPNNV | SVTSSGVQLT | VAMRNVPDLS | LGVSCSFEEV | TESEAILLPS | GELRCPSPSL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| QELQTLTRGH | GATHTVRLQL | LSMETGVRFA | GVDFVFYNCS | ALQSCMSCVG | SPYPCHWCKY |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| RHVCTSHPHE | CSFQEGRVHS | PEGCPEILPR | GDLLIPVGVM | QPLTLRAKNL | PQPQSGQKNY |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ECVVRVQGRQ | HRVPAVRFNS | SSVQCQNASY | FYEGDEFGDT | ELDFSVVWDG | DFPIDKPPSF |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| RALLYKCWAQ | RPSCGLCLKA | DPRFNCGWCI | SEHRCQLRVH | CPAPKSNWMH | PSQKGARCSH |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| PRITQIHPLT | GPKEGGTRVT | IVGENLGLTS | REVGLRVAGV | RCNSIPTEYV | SAERIVCEME |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| ESLVPSPPPG | PAELCVGDCS | ADFRTQSQQL | YSFVTPTLDR | VSPTRGPASG | GTRLTISGTS |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| LDAGSRVTVI | IRDGECQFVR | RDAEAIVCIS | PISTLGPSQA | PIILAIDHAN | ISSTGVIYTY |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| TQDPTVTHLE | PTWSIINGST | SITVSGTHLL | TVQEPRVRAK | YRGIETTNTC | QVINDTAMLC |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| KAPGIFLGHP | QPRAQGEHPD | EFGFLLDHVQ | AARSLNRSSF | TYYPDPSFEP | LGPSGVLDVK |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| PGSHVVLKGK | NLIPAAAGSS | RLNYTVLIGG | QPCALTVSDT | QLLCDSPSQT | GRQPVMVLVG |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| GLEFWLGTLH | ITADRALTLP | AMVGLAAGGG | LLLLAITVVL | VAYKRKTQDA | DRTLKRLQLQ |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| MDNLESRVAL | ECKEAFAELQ | TDINELTNHM | DGVQIPFLDY | RTYAVRVLFP | GIEAHPVLKE |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| LDTPPNVEKA | LRLFGQLLHS | RAFLLTFIHT | LEAQSSFSMR | DRGTVASLTM | VALQSRLDYA |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| TGLLKQLLAD | LIEKNLESKN | HPKLLLRRTE | SVAEKMLTNW | FTFLLHKFLK | ECAGEPLFLL |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| YCAIKQQMEK | GPIDAITGEA | RYSLSEDKLI | RQQIDYKTLT | LHCVCPESEG | SAQVPVKVLN |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| CDSITQAKDK | LLDTVYKGIP | YSQRPKAEDM | DLEWRQGRMA | RIILQDEDIT | TKIECDWKRI |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| NSLAHYQVTD | GSLVALVPKQ | VSAYNMANSF | TFTRSLSRYE | SLLRAASSPD | SLRSRAPMLT |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | 1660 | 1670 | 1680 |
| PDQEAGTKLW | HLVKNHDHAD | HREGDRGSKM | VSEIYLTRLL | ATKGTLQKFV | DDLFETVFST |
| 1690 | 1700 | 1710 | 1720 | 1730 | 1740 |
| AHRGSALPLA | IKYMFDFLDE | QADQRQISDP | DVRHTWKSNC | LPLRFWVNVI | KNPQFVFDIH |
| 1750 | 1760 | 1770 | 1780 | 1790 | 1800 |
| KNSITDACLS | VVAQTFMDSC | STSEHRLGKD | SPSNKLLYAK | DIPNYKSWVE | RYYRDIAKMA |
| 1810 | 1820 | 1830 | 1840 | 1850 | 1860 |
| SISDQDMDAY | LVEQSRLHAN | DFNVLSALSE | LYFYVTKYRQ | EILTSLDRDA | SCRKHKLRQK |
| 1870 | |||||
| LEQIITLVSS | SS |