B8XX90
Gene name |
STING1 |
Protein name |
Stimulator of interferon genes protein |
Names |
poSTING, Transmembrane protein 173 |
Species |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
KEGG Pathway |
ssc:100217389 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
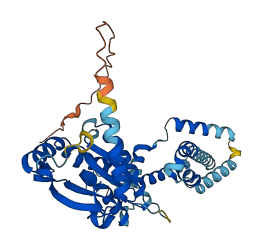
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
154-337 (Cytosolic c-di-GMP binding domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

No variants for B8XX90
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for B8XX90 | |||||
No associated diseases with B8XX90
1 regional properties for B8XX90
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Stimulator of interferon genes protein, C-terminal | 154 - 337 | IPR047191 |
Functions
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an autophagosome, a double-membrane-bounded vesicle in which endogenous cellular material is sequestered. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Golgi intermediate compartment system. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| mitochondrial outer membrane | The outer, i.e. cytoplasm-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP binding | Binding to 2',3' cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) nucleotide, a cyclic purine dinucleotide that consists of AMP and GMP units cyclized via 2',5' and 3',5' linkages. |
| cyclic-di-GMP binding | Binding to cyclic-di-GMP, cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
8 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of innate immune response | Any process that initiates an innate immune response. Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. Examples of this process include activation of the hypersensitive response of Arabidopsis thaliana and activation of any NOD or TLR signaling pathway in vertebrate species. |
| autophagosome assembly | The formation of a double membrane-bounded structure, the autophagosome, that occurs when a specialized membrane sac, called the isolation membrane, starts to enclose a portion of the cytoplasm. |
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| positive regulation of interferon-beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-beta production. |
| positive regulation of macroautophagy | Any process, such as recognition of nutrient depletion, that activates or increases the rate of macroautophagy to bring cytosolic macromolecules to the vacuole/lysosome for degradation. |
| positive regulation of type I interferon production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of type I interferon production. Type I interferons include the interferon-alpha, beta, delta, episilon, zeta, kappa, tau, and omega gene families. |
| reticulophagy | The selective autohagy process in which parts of the endoplasmic reticulum are loaded into autophagosomes, delivered to the vacuole, and degraded in response to changing cellular conditions. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2KI99 | STING1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| E1C7U0 | STING1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q86WV6 | STING1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q3TBT3 | Sting1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| F1M391 | Sting1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPYSSLHPSI | PQPRGLRAQV | AALVLLGACL | VALWGLGELP | EYTLRWLVLH | LASQQIGLLV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KGLCSLAEEL | CHVHSRYQSS | YWRAARACLG | CPIRCGALLL | LSCYFYFSIR | DKAGLPLPWM |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LALLGLSQAL | NILLGLQHLA | PAEVSAICEK | RNFNVAHGLA | WSYYIGYLRL | ILPGLRARIQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| AYNQRHKNVL | GGIGNHRLHI | LFPLDCGVPD | DLSVADPNIR | FLHELPQQSA | DRAGIKGRVY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TNSIYELLEN | GQPAGVCVLG | YATPLQTLFA | MSQDGRAGFS | REDRLEQAKL | FCRTLEDILA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DAPEAQNNCR | LIVYQEPTEG | GSFSLSQEIL | RHLRQEEREV | TMGSAETSVV | PTSSTLSQEP |
| 370 | |||||
| ELLISGMEQP | LPLRSDIF |