Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
154-419 (Peptidase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
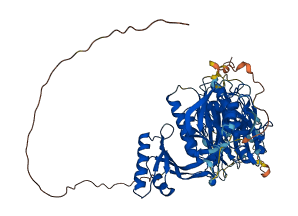
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for A8T658
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-A8T658-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for A8T658
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for A8T658 | |||||
No associated diseases with A8T658
4 regional properties for A8T658
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Peptidase S8 propeptide/proteinase inhibitor I9 | 75 - 147 | IPR010259 |
| domain | Proteinase K-like catalytic domain | 154 - 419 | IPR034193 |
| domain | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, C-terminal domain 2 | 533 - 598 | IPR041052 |
| domain | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, C-terminal domain 1 | 448 - 529 | IPR041254 |
Functions
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| lysosome | A small lytic vacuole that has cell cycle-independent morphology found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases, most of which have their maximal activities in the pH range 5-6. The contained enzymes display latency if properly isolated. About 40 different lysosomal hydrolases are known and lysosomes have a great variety of morphologies and functions. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apolipoprotein binding | Binding to an apolipoprotein, the protein component of a lipoprotein complex. |
| low-density lipoprotein particle binding | Binding to a low-density lipoprotein particle, a lipoprotein particle that is rich in cholesterol esters and low in triglycerides, is typically composed of APOB100 and APOE, and has a density of 1.02-1.06 g/ml and a diameter of between 20-25 nm. |
| protein self-association | Binding to a domain within the same polypeptide. |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine). |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle binding | Binding to a very-low-density lipoprotein particle, a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle that is typically composed of APOB100, APOE and APOCs and has a density of about 1.006 g/ml and a diameter of between 20-80 nm. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| cholesterol metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. It is a component of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer and of plasma lipoproteins and can be found in all animal tissues. |
| low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a low-density lipoprotein particle receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGTVSSRRSW | WPLPLLLLLL | LGPAGARAQE | DEDGDYEELV | LALRSEEDGL | AEAPEHGATA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TFHRCAKDPW | RLPGTYVVVL | KEETHRSQSE | RTARRLQAQA | ARRGYLTKIL | HVFHDLLPGF |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LVKMSGDLLE | LALKLPHVDY | IEEDSSVFAQ | SIPWNLERIT | PPRYRADEYQ | PPDGGSLVEV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| YLLDTSIQSD | HREIEGRVMV | TDFENVPEED | GTRFHRQASK | CDSHGTHLAG | VVSGRDAGVA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KGASMRSLRV | LNCQGKGTVS | GTLIGLEFIR | KSQLVQPVGP | LVVLMPLAGG | YSRVLNAACQ |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RLARAGVVLV | TAAGNFRDDA | CLYSPASAPE | VITVGATNAQ | DQPVTLGTLG | TNFGRCVDLF |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| APGEDIIGAS | SDCSTCFVSQ | SGTSQAAAHV | AGIAAMMLSV | EPELTLAELR | QRLIHFSAKD |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VINEVWFPED | QRVLTPNLVA | ALPPSTHGAG | WQLFCRTVWS | AHSGPTRMAT | AIARCAPDEE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LLSCSSFSRS | GKRRGERMEA | QGGKLVCRAH | NAFGGEGVCA | IARCCLLPQA | NCSVHTAPPA |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| GSGMGTRVLC | HQQVHVLTGC | SSHWEVEDLG | THKPPVLRPR | GQPNQCVGHR | EASIHASCCR |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| APGLECKVKE | HGIPAPQEQV | TVACEEGWTL | TGCSALPGTS | HVLGAYAVDN | TCVVRSRDIS |
| 670 | 680 | ||||
| TTGSTSEEAM | AAVAICCRRR | HLAQASQELQ |