A2A825
Gene name |
Cplane2 (Gm723, Rsg1) |
Protein name |
Ciliogenesis and planar polarity effector 2 |
Names |
REM2- and Rab-like small GTPase 1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:76166 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
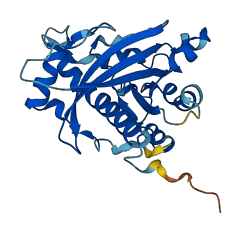
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for A2A825
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7Q3E | EM | 335 A | D | 1-258 | PDB |
| AF-A2A825-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
13 variants for A2A825
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs864308532 | 24 | Y>H | No | EVA | |
| rs27571372 | 40 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3395057424 | 63 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3394913587 | 63 | K>T | No | EVA | |
| rs27556364 | 106 | C>R | No | EVA | |
| rs264250383 | 114 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388726190 | 146 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388732289 | 148 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs27556360 | 168 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388712510 | 184 | D>H | No | EVA | |
| rs27556358 | 187 | A>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388704276 | 190 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388727513 | 258 | G>D | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with A2A825
No regional properties for A2A825
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for A2A825 | |||
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| centriole | A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle. |
| ciliary basal body | A membrane-tethered, short cylindrical array of microtubules and associated proteins found at the base of a eukaryotic cilium (also called flagellum) that is similar in structure to a centriole and derives from it. The cilium basal body is the site of assembly and remodelling of the cilium and serves as a nucleation site for axoneme growth. As well as anchoring the cilium, it is thought to provide a selective gateway regulating the entry of ciliary proteins and vesicles by intraflagellar transport. |
| ciliary base | Area of the cilium (also called flagellum) where the basal body and the axoneme are anchored to the plasma membrane. The ciliary base encompasses the distal part of the basal body, transition fibers and transition zone and is structurally and functionally very distinct from the rest of the cilium. In this area proteins are sorted and filtered before entering the cilium, and many ciliary proteins localize specifically to this area. |
| ciliary transition zone | A region of the cilium between the basal body and proximal segment that is characterized by Y-shaped assemblages that connect axonemal microtubules to the ciliary membrane. The ciliary transition zone appears to function as a gate that controls ciliary membrane composition and separates the cytosol from the ciliary plasm. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
13 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axoneme assembly | The assembly and organization of an axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia (also called flagella) in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements. |
| cilium assembly | The assembly of a cilium, a specialized eukaryotic organelle that consists of a filiform extrusion of the cell surface. Each cilium is bounded by an extrusion of the cytoplasmic membrane, and contains a regular longitudinal array of microtubules, anchored basally in a centriole. |
| cranial skeletal system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cranial skeletal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The cranial skeletal system is the skeletal subdivision of the head, and includes the skull (cranium plus mandible), pharyngeal and/or hyoid apparatus. |
| endocardial cushion fusion | The cell-cell adhesion process of mesenchymal cardiac cushion cells that contributes to the process of cushion shaping. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| limb development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a limb over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. Examples include legs, arms or some types of fin. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| protein processing | Any protein maturation process achieved by the cleavage of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein. Protein maturation is the process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| regulation of smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning. |
| regulation of vesicle fusion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of vesicle fusion. |
| smoothened signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of activation of the transmembrane protein Smoothened. |
34 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P08642 | HRAS | GTPase HRas | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P11233 | RALA | Ras-related protein Ral-A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6T310 | RASL11A | Ras-like protein family member 11A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P01116 | KRAS | GTPase KRas | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P62070 | RRAS2 | Ras-related protein R-Ras2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IYK8 | REM2 | GTP-binding protein REM 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P11234 | RALB | Ras-related protein Ral-B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P55040 | GEM | GTP-binding protein GEM | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99578 | RIT2 | GTP-binding protein Rit2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6IQ22 | RAB12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96HU8 | DIRAS2 | GTP-binding protein Di-Ras2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P01112 | HRAS | GTPase HRas | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BU20 | CPLANE2 | Ciliogenesis and planar polarity effector 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9JIW9 | Ralb | Ras-related protein Ral-B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61411 | Hras | GTPase HRas | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P32883 | Kras | GTPase KRas | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O08989 | Mras | Ras-related protein M-Ras | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5PR73 | Diras2 | GTP-binding protein Di-Ras2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91Z61 | Diras1 | GTP-binding protein Di-Ras1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P62071 | Rras2 | Ras-related protein R-Ras2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35283 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q08AT1 | Rasl12 | Ras-like protein family member 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55041 | Gem | GTP-binding protein GEM | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70425 | Rit2 | GTP-binding protein Rit2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VEL9 | Rem2 | GTP-binding protein REM 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P36860 | Ralb | Ras-related protein Ral-B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P08644 | Kras | GTPase KRas | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WTY2 | Rem2 | GTP-binding protein REM 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P20171 | Hras | GTPase HRas | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q5BJQ5 | Rit2 | GTP-binding protein Rit2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P97538 | Mras | Ras-related protein M-Ras | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| B7ZTR0 | cplane2 | Ciliogenesis and planar polarity effector 2 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| P79737 | nras | GTPase NRas | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| A1DZY4 | zgc:110179 | Ras-like protein family member 11A-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MARPPMHGSV | IVPDWHETVE | GKEYLACILR | KNRRREFGLL | ERPVLPPSVV | IDTASYKIFV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SGKSGVGKTA | LVAKLAGLEV | PIVHHETTGI | QTTVVFWPAK | LKASDCVVMF | RFEFWDCGES |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| ALKKFDHMLP | ACKENADAFL | FLFSFTDRAS | FEDLPGQLTR | VAGEAPGLVK | IVIGSKFDQY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| MHTDVPARDL | TAFRQAWELP | LFRVKSVPGR | RLADGRTLDG | RAGLADTAHV | LNGLAEQLWH |
| 250 | |||||
| QDQVAAGLLP | SSPESAPG |