A0A544CH04
Gene name |
rfaH (FLM02_01525) |
Protein name |
Transcription antitermination protein RfaH |
Names |
|
Species |
Vibrio cholerae |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
RHO-INTERACTING TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSG (PTHR30265) |
Descriptions
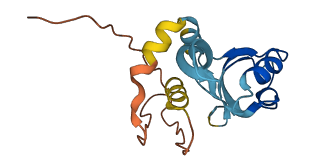
Transcription antitermination protein RfaH is an operon-specific paralog of NusG and consists of an NGN domain that is connected to a KOW domain via a flexible linker. In free RfaH, KOW domain folds as an α-helical hairpin that interacts with the NGN domain, which masks the binding site for RNA polymerase (RNAP) at the interface on the NGN domain (autoinhibited state). Upon recruitment to a transcription elongation complex pausing at an operon polarity suppressor (ops) site, RfaH is activated by dissociating and refolding the liberated KOW domain into β-barrel state, which enhances distal genes transcription elongation in a specialized subset of operons that encode extracytoplasmic components, and serves as recruitment platform for ribosomes to activate activation. Upon release from RNAP, RfaH is transformed back into its autoinhibited state.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-101 (NGN-like domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for A0A544CH04
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-A0A544CH04-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for A0A544CH04
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for A0A544CH04 | |||||
No associated diseases with A0A544CH04
No regional properties for A0A544CH04
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for A0A544CH04 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR30265 | RHO-INTERACTING TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSG |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR30265:SF7 | TRANSCRIPTION ANTITERMINATION PROTEIN RFAH |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
No GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for cellular component |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| transcription antitermination factor activity, DNA binding | Binds to DNA, typically within region of the promoter and transcribed region, to promote readthrough of a transcription termination site and thus extending the length of the RNA transcript produced. Examples of antitermination factors which bind DNA include the lambda Q protein. |
1 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling | A chromatin remodeling process that reestablishes the chromatin structure following the passage of RNA polymerase II during transcription elongation, thus preventing cryptic transcription initiation. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKRWYLLYCK | RGEQQRAKMH | LENQSVECFY | PEVCVEKILR | GKRQIVQEPL | FPSYMFVRFD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FENGPSFTTV | RSTRGVVDFV | RLGPHPRELQ | GDLIYQLKQL | DCEQLKHATK | QLPEKGQTVR |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | ||
| VARGQFAGIE | AIYLEPDGDT | RSIMLVKMIS | QQVPMSIENT | DWEVT |