A0A377U130
Gene name |
NCTC9140_07377 |
Protein name |
RNA polymerase sigma-54 factor |
Names |
|
Species |
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
RNA POLYMERASE SIGMA-54 FACTOR (PTHR32248) |
Descriptions
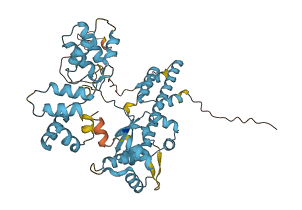
Autoinhibition in sigma factors is regulated by domain movements that control DNA delivery into the RNA polymerase active site. This process is essential for gene transcription regulation, particularly in response to environmental stress. Autoinhibited sigma factors undergo remodeling by activator proteins through ATP hydrolysis, enabling the transition from a closed promoter complex to an open one, facilitating transcription initiation. The region I of sigma factor 54 plays a crucial regulatory role in maintaining the closed promoter complex by forming a network of interactions both with the -12 promoter element and with the region III, thus preventing spontaneous conversion from the closed promoter complex to the open promoter complex.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
108-477 (Region III, DNA binding domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for A0A377U130
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-A0A377U130-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for A0A377U130
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for A0A377U130 | |||||
No associated diseases with A0A377U130
No regional properties for A0A377U130
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for A0A377U130 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR32248 | RNA POLYMERASE SIGMA-54 FACTOR |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR32248:SF4 | RNA POLYMERASE SIGMA-54 FACTOR |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
helix-turn-helix transcription factor
Sigma factor |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex | A protein complex that possesses DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets. |
| nucleotidyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a nucleotidyl group to a reactant. |
| sigma factor activity | Sigma factors act as the promoter specificity subunit of eubacterial and plant plastid multisubunit RNA polymerases, whose core subunit composition is often described as alpha(2)-beta-beta-prime. Although sigma does not bind DNA on its own, when combined with the core to form the holoenzyme, the sigma factor binds specifically to promoter elements. The sigma subunit is released once elongation begins. |
1 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-templated transcription initiation | The initial step of transcription, consisting of the assembly of the RNA polymerase preinitiation complex (PIC) at a gene promoter, as well as the formation of the first few bonds of the RNA transcript. Transcription initiation includes abortive initiation events, which occur when the first few nucleotides are repeatedly synthesized and then released, and ends when promoter clearance takes place. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKQGLQLRLS | QQLAMTPQLQ | QAIRLLQLST | LELQQELQQA | LESNPLLEQT | DLHDEVEAKE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VEDRESLDTV | DALEQKEMPD | ELPLDASWDE | IYTAGTPSGN | GVDYQDDELP | VYQGETTQTL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QDYLMWQVEL | TPFTDTDRAI | ATSIVDAVDD | TGYLTIQIED | IVDSIGDDEI | GLEEVEAVLK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RIQRFDPVGV | AAKDLRDCLL | IQLSQFAKET | PWLEEARLII | SDHLDLLANH | DFRTLMRVTR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LKEEVLKEAV | NLIQSLDPRP | GQSIQTSEPE | YVIPDVLVRK | VSGRWTVELN | ADSIPRLKIN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QQYAAMGNSA | RNDADGQFIR | SNLQEARWLI | KSLESRNDTL | LRVSRCIVEQ | QQAFFEQGEE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| YMKPMVLADI | AQAVEMHEST | ISRVTTQKYL | HSPRGIFELK | YFFSSHVNTE | GGGEASSTAI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | |
| RALVKKLIAA | ENPAKPLSDS | KLTSMLSEQG | IMVARRTVAK | YRESYPSRRQ | TSVNNWV |