A0A0H3LK99
Gene name |
BB1184 |
Protein name |
Putative exported protein |
Names |
|
Species |
Bordetella bronchiseptica (Alcaligenes bronchisepticus) |
KEGG Pathway |
bbr:BB1184 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
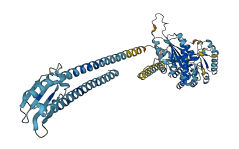
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
419-658 (EAL domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for A0A0H3LK99
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-A0A0H3LK99-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for A0A0H3LK99
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for A0A0H3LK99 | |||||
No associated diseases with A0A0H3LK99
8 regional properties for A0A0H3LK99
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | EF-hand domain | 42 - 92 | IPR002048-1 |
| domain | EF-hand domain | 97 - 200 | IPR002048-2 |
| domain | FAD-binding 8 | 446 - 574 | IPR013112 |
| domain | Ferric reductase, NAD binding domain | 583 - 753 | IPR013121 |
| domain | Ferric reductase transmembrane component-like domain | 272 - 413 | IPR013130 |
| domain | FAD-binding domain, ferredoxin reductase-type | 441 - 577 | IPR017927 |
| binding_site | EF-Hand 1, calcium-binding site | 70 - 82 | IPR018247-1 |
| binding_site | EF-Hand 1, calcium-binding site | 178 - 190 | IPR018247-2 |
25 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction | A cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex. The epithelial cadherins, or E-cadherins, of each interacting cell extend through the plasma membrane into the extracellular space and bind to each other. The E-cadherins bind to catenins on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, where the E-cadherin-catenin complex binds to cytoskeletal components and regulatory and signaling molecules. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic shaft | Cylindric portion of the dendrite, directly stemming from the perikaryon, and carrying the dendritic spines. |
| dendritic spine cytoplasm | The region of the neuronal cytoplasm located in dendritic spines. |
| excitatory synapse | A synapse in which an action potential in the presynaptic cell increases the probability of an action potential occurring in the postsynaptic cell. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| filopodium | Thin, stiff, actin-based protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal or dendritic growth cone, or a dendritic shaft. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| neuron projection branch point | The location where a secondary projection arises from a neuron projection. |
| neuron projection terminus | The specialized, terminal region of a neuron projection such as an axon or a dendrite. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the postsynapse. |
| postsynaptic density, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane forming an electron dense disc. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| presynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the presynapse. |
| rough endoplasmic reticulum | The rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum (ER) has ribosomes adhering to the outer surface; the ribosomes are the site of translation of the mRNA for those proteins which are either to be retained within the cisternae (ER-resident proteins), the proteins of the lysosomes, or the proteins destined for export from the cell. Glycoproteins undergo their initial glycosylation within the cisternae. |
| ruffle | Projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell; the protrusions are supported by a microfilament meshwork. |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
| secretory granule | A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules. |
| synaptic membrane | A specialized area of membrane on either the presynaptic or the postsynaptic side of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion | Any cadherin binding that occurs as part of the process of cell-cell adhesion. |
| cytoskeletal anchor activity | The binding activity of a protein that brings together a cytoskeletal protein (either a microtubule or actin filament, spindle pole body, or protein directly bound to them) and one or more other molecules, permitting them to function in a coordinated way. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| proline-rich region binding | Binding to a proline-rich region, i.e. a region that contains a high proportion of proline residues, in a protein. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| transcription coregulator binding | Binding to a transcription coregulator, a protein involved in regulation of transcription via protein-protein interactions with transcription factors and other transcription regulatory proteins. Cofactors do not bind DNA directly, but rather mediate protein-protein interactions between regulatory transcription factors and the basal transcription machinery. |
20 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin crosslink formation | The process in which two or more actin filaments are connected together by proteins that act as crosslinks between the filaments. The crosslinked filaments may be on the same or differing axes. |
| actin filament bundle assembly | The assembly of actin filament bundles; actin filaments are on the same axis but may be oriented with the same or opposite polarities and may be packed with different levels of tightness. |
| axonogenesis | De novo generation of a long process of a neuron, including the terminal branched region. Refers to the morphogenesis or creation of shape or form of the developing axon, which carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells. |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an epidermal growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to L-glutamate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a L-glutamate(1-) stimulus. |
| dendrite development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendrite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| insulin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the insulin receptor binding to insulin. |
| modification of synaptic structure, modulating synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates synaptic transmission via modification of the structure of the synapse. |
| plasma membrane organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the plasma membrane. |
| positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of actin cytoskeleton reorganization. |
| positive regulation of actin filament polymerization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of actin polymerization. |
| positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of dendritic spine morphogenesis, the process in which the anatomical structures of a dendritic spine are generated and organized. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential | Any process that enhances the establishment or increases the extent of the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) which is a temporary increase in postsynaptic potential due to the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) and makes it easier for the neuron to fire an action potential. |
| protein localization to synapse | Any process in which a protein is transported to, and/or maintained at the synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton. |
| regulation of synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| response to bacterium | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSILRRLLLS | LTLAIGIILL | GTLVLSINAA | RGYLSDQLQV | QSTDAAVSLA | LSLSQPANND |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PVTQELLVSA | LFDGGHFSLV | RLADPQGAVM | VERGAQPAAS | VPAWFQALAP | LANRAASHAV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SDGWRQIGEV | TLVANDAYAW | ETLWASSLRM | AALIMGAGVL | WALFAFALVR | WIEKRLLFQV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SEQVRAIDSR | ASGEQAFARV | AEFSGIVDAL | AQTRERVRAT | AEEQSSRIES | LEVELNQDPV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TGLANRKYFI | NEFRRALDEK | PADSPALPAR | LSSAGGHVLV | FRQRDLTALN | RHMPRQFIDQ |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| WLQSVCQRIS | ALVTAQGLAQ | SLVARLNGSD | FAVLLPHCAA | PQAQVIADLV | RAELRTLRIP |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VGEGGLCRWA | MALADYAPGT | QFNGVLARLD | FGLTRAESAG | DDHAVLVGPD | NADPFSAAGQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SAWMDALVTA | LDQQRFSLAF | EPLHAVDGRL | VRMEAMLMLH | NDDAREPIPA | MLFIPAAVRL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NLSAECDLQA | VRLALDWLAA | QPGELAVRLS | LPSLGKRSFL | RQLELMLADR | RAQVGRLYLE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VDAHGLVDRE | GDVIALERIA | AHFGAHVGLR | RLAQQFGAMS | RLHSLPLAYV | KLGGGFVGGM |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | |
| SQSPGSRQLA | GSVIDTARAL | NIDVYAEDVP | DAATRDILAS | MGVEVMRGPG | VTPPPAQE |