A0A044RE18
Gene name |
Bli |
Protein name |
Endoprotease bli |
Names |
Blisterase |
Species |
Onchocerca volvulus |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
3.4.21.75: Serine endopeptidases |
Protein Class |
PROPROTEIN CONVERTASE SUBTILISIN/KEXIN-RELATED (PTHR42884) |
Descriptions
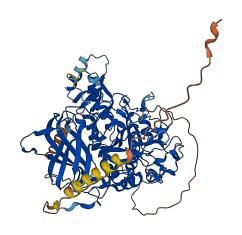
Bli is a subtilisin-like proprotein convertase of nematodes. For its activation, its N-terminal prodomain should be cleaved at the RRKR motif. After cleavage, the prodomain remains associated with the protease, inhibiting its catalytic domain until the complex is translocated to the trans Golgi network. Once in the Golgi apparatus, the prodomain dissociates from the mature enzyme upon cleavage. Independent expression of the prodomain is able to inhibit the activity of the catalytic domain.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
159-447 (Kexin/furin catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for A0A044RE18
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-A0A044RE18-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for A0A044RE18
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for A0A044RE18 | |||||
No associated diseases with A0A044RE18
6 regional properties for A0A044RE18
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Peptidase S8/S53 domain | 192 - 474 | IPR000209 |
| domain | P domain | 490 - 628 | IPR002884 |
| active_site | Peptidase S8, subtilisin, His-active site | 240 - 250 | IPR022398 |
| active_site | Peptidase S8, subtilisin, Asp-active site | 197 - 208 | IPR023827 |
| domain | Peptidase S8, pro-domain | 42 - 116 | IPR032815 |
| domain | Kexin/furin catalytic domain | 159 - 447 | IPR034182 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.4.21.75 | Serine endopeptidases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR42884 | PROPROTEIN CONVERTASE SUBTILISIN/KEXIN-RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR42884:SF23 | FURIN-LIKE PROTEASE 2 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
serine protease
protein modifying enzyme |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Endothelin signaling pathway furin Alzheimer disease-presenilin pathway Furin Alzheimer disease-amyloid secretase pathway Furin |
|
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine). |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to salt | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a salt stimulus. |
| chemosensory behavior | Behavior that is dependent upon the sensation of chemicals. |
| collagen and cuticulin-based cuticle development | Synthesis and deposition of a collagen and cuticulin-based noncellular, hardened, or membranous secretion from an epithelial sheet. An example of this process is found in Caenorhabditis elegans. |
| dibasic protein processing | Any protein processing achieved by the cleavage of a peptide bond after two basic amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction. |
| zymogen activation | The proteolytic processing of an inactive enzyme to an active form. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MYWQLVRILV | LFDCLQKILA | IEHDSICIAD | VDDACPEPSH | TVMRLRERND | KKAHLIAKQH |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GLEIRGQPFL | DGKSYFVTHI | SKQRSRRRKR | EIISRLQEHP | DILSIEEQRP | RVRRKRDFLY |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PDIAHELAGS | STNIRHTGLI | SNTEPRIDFI | QHDAPVLPFP | DPLYKEQWYL | NNGAQGGFDM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| NVQAAWLLGY | AGRNISVSIL | DDGIQRDHPD | LAANYDPLAS | TDINGHDDDP | TPQDDGDNKH |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GTRCAGEVAS | IAGNVYCGVG | VAFHAKIGGV | RMLDGPVSDS | VEAASLSLNR | HHIDIYSASW |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GPEDDGRTFD | GPGPLAREAF | YRGVKAGRGG | KGSIFVWASG | NGGSRQDSCS | ADGYTTSVYT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LSVSSATIDN | RSPWYLEECP | STIATTYSSA | NMNQPAIITV | DVPHGCTRSH | TGTSASAPLA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| AGIIALALEA | NPNLTWRDMQ | HIVLRTANPV | PLLNNPGWSV | NGVGRRINNK | FGYGLMDAGA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LVKLALIWKT | VPEQHICTYD | YKLEKPNPRP | ITGNFQMNFS | LEVNGCESGT | PVLYLEHVQV |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LATFRFGKRG | DLKLTLFSPR | GTSSVLLPPR | PQDFNSNGIH | KWPFLSVQTW | GEDPRGKWTL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| MVESVSTNRN | VGGTFHDWSL | LLYGTAEPAQ | PNDPRHSSVV | PSSVSAESPF | DRITQHIASQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | |||
| EKKKKQRDSR | DWQPKKVENK | KSLLVSAQPE | LRV |